Importance of Extrusion in Artificial Grass
The extrusion process allows manufacturers to create fibers that closely resemble the natural texture and appearance of grass. The ability to manipulate the polymer material during extrusion means that different textures can be achieved to mimic the subtle variations found in natural grass blades. Real grass is not uniform in texture or color; it varies in thickness, curl, and bend, which gives it a lifelike, organic look. Similarly, artificial grass can be designed to replicate these natural variations, making the synthetic turf more convincing and realistic.
By controlling the extrusion die and temperature settings, manufacturers can produce fibers with different shapes and thicknesses, such as flat, oval, or round blades. Flat blades often replicate the appearance of real grass blades, which are naturally wide and flat, while oval or round blades may provide a denser, more uniform look. The arrangement of the fibers and their orientation further enhances the natural feel of the artificial grass, making it appear more authentic when viewed from different angles.
Additionally, manufacturers can introduce slight twists and bends in the fibers during extrusion to simulate the way real grass naturally moves and bends with the wind or when stepped on. This added flexibility creates a natural bounce and resilience in the fibers, contributing to the overall visual appeal and tactile experience of the turf.
Color Customization for Realism
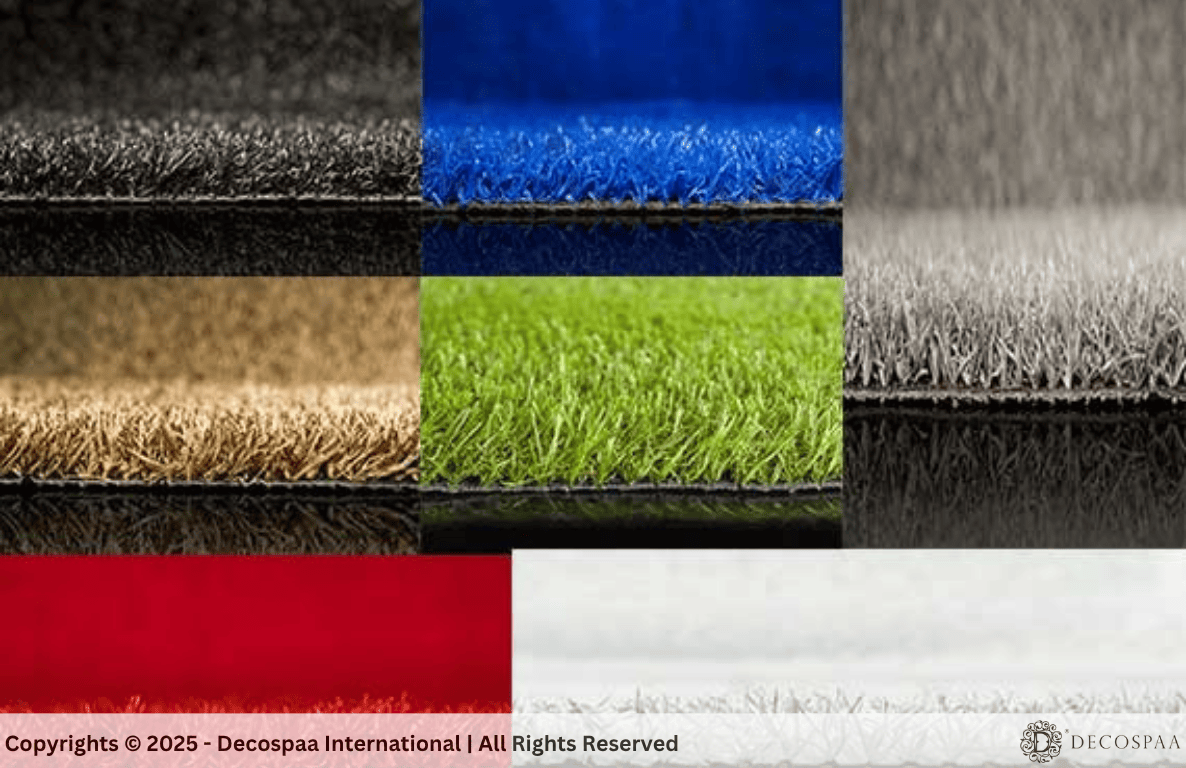
One of the most remarkable aspects of the extrusion process is the ability to introduce multiple colors and shades into the synthetic fibers. Real grass is rarely a single uniform color; it has natural variations due to sunlight exposure, seasonal changes, and environmental factors. To replicate this, manufacturers mix and blend a variety of color pigments, most commonly in shades of emerald green, olive green, and lime green, to achieve a multi-dimensional look.
For instance, the blending of emerald green with olive green mimics the deep hues of healthy, mature grass, while lime green can add highlights, simulating the fresh, vibrant look of spring grass. Some artificial grass products also incorporate yellow, brown, or tan fibers to replicate the appearance of grass in different seasons, such as the fading grass seen in late summer or fall.
These carefully chosen colors not only make the turf appear more natural, but they also contribute to the turf's ability to blend seamlessly into its surroundings, whether it's part of a landscape in a residential garden, a sports field, or a commercial project. The multi-dimensional color mix ensures that the grass looks realistic under varying light conditions, whether in bright sunlight or shaded areas, offering the same visual depth found in natural grass.
Durability and Resistance to Environmental
The extrusion process is also key to ensuring the durability and performance of the artificial grass under harsh environmental conditions. The synthetic fibers created during extrusion are engineered to be highly resistant to UV rays, wear and tear, and extreme weather. This is achieved through the addition of UV stabilizers and anti-aging agents during the material preparation stage, which help to prevent fading and maintain the vibrancy of the grass fibers even after prolonged exposure to the sun.
UV resistance is particularly important because artificial grass is typically installed outdoors, where it is exposed to direct sunlight for long periods. Without UV stabilizers, the synthetic fibers would degrade, causing the grass to lose its color and structural integrity.
Flexibility and Performance
The extrusion process also plays a significant role in enhancing the flexibility and performance of the artificial grass. By manipulating the polymer’s molecular structure during extrusion, manufacturers can create fibers that have varying degrees of rigidity and softness. This allows the grass to not only feel comfortable underfoot but also to have the necessary resilience to recover from the impact of foot traffic, sports activities, or even pets running on the surface.
For applications like sports fields or public parks, flexibility is essential, as the grass must be able to withstand frequent use without becoming flattened or worn down. The fibers are engineered to bounce back after compression, which ensures that the grass maintains its thickness and natural appearance over time, even after heavy use
Aesthetic and Functional Innovation
The extrusion process has led to significant innovation in both the aesthetic and functional aspects of artificial grass. Beyond traditional green grass, modern artificial turf options are available in various colors and textures, making them adaptable to a wide range of applications, from landscaping to sporting fields and even decorative purposes. The ability to combine various fiber types and colors, along with the advanced manufacturing technologies involved, has enabled manufacturers to produce synthetic grass products that not only mimic natural grass in appearance but also meet the practical needs of various industries.
For instance, turf designed for football or hockey can feature fibers with specialized characteristics, such as increased traction or ball control. Similarly, artificial grass used in landscaping can be tailored to provide a more natural, varied appearance, replicating the look of wild grass or golf course grass. This allows artificial grass to be customized for nearly any outdoor space, enhancing both its aesthetic value and its practical functionality.
The Future of Artificial Grass
Early Innovation and High-Performance Turf Material
Properties of Nylon (PA) in Artificial Grass
Advantages of Nylon in High-Traffic Applications
The durability, strength, and resilience of nylon make it highly suited for sports applications, especially in high-traffic areas where the grass will experience constant compression and wear. For example, football fields, rugby pitches, and hockey rinks benefit significantly from the toughness of nylon fibers. These fields are often used for intense, high-impact activities, including constant running, falling, and contact sports, all of which demand a material that can withstand such force without becoming damaged.
In these contexts, nylon's ability to retain its shape and bounce back after heavy compression means that the turf continues to perform at a high level throughout the season, without developing permanent flattened spots or fibers that lose their integrity over time.
Challenges of Nylon in Artificial Grass
While nylon offers significant performance benefits, there are a few drawbacks that have led to its eventual replacement in many residential and commercial applications:
1. Cost:- Nylon is more expensive to produce than other synthetic fibers like polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE), which has made it a less popular choice for large-scale projects or areas where cost-effectiveness is a priority. The cost of producing nylon fibers can be quite high, making it more suitable for premium applications or situations where performance is prioritized over cost.
2. Weight:- Nylon fibers are relatively heavy compared to other materials, which can increase the weight of the turf and make it more challenging to install and maintain. This factor can be particularly problematic for areas that require extensive coverage or need to be transported over long distances.
The Modern Standards for Artificial Grass
Lightweight and Flexible
Polypropylene (PP) has become a key material in artificial grass production, especially for residential and light-traffic areas. PP is a highly lightweight polymer, which contributes to lower transportation costs and easier installation. The material is also flexible and moisture-resistant, which helps the turf retain its shape and performance even in areas with moderate wear and tear.
However, polypropylene is typically more suitable for lighter use areas. It lacks the high-level durability and strength provided by other polymers like nylon (PA) or polyethylene (PE), making it less ideal for high-traffic environments.
Extrusion Process: From Pellets to Fibers
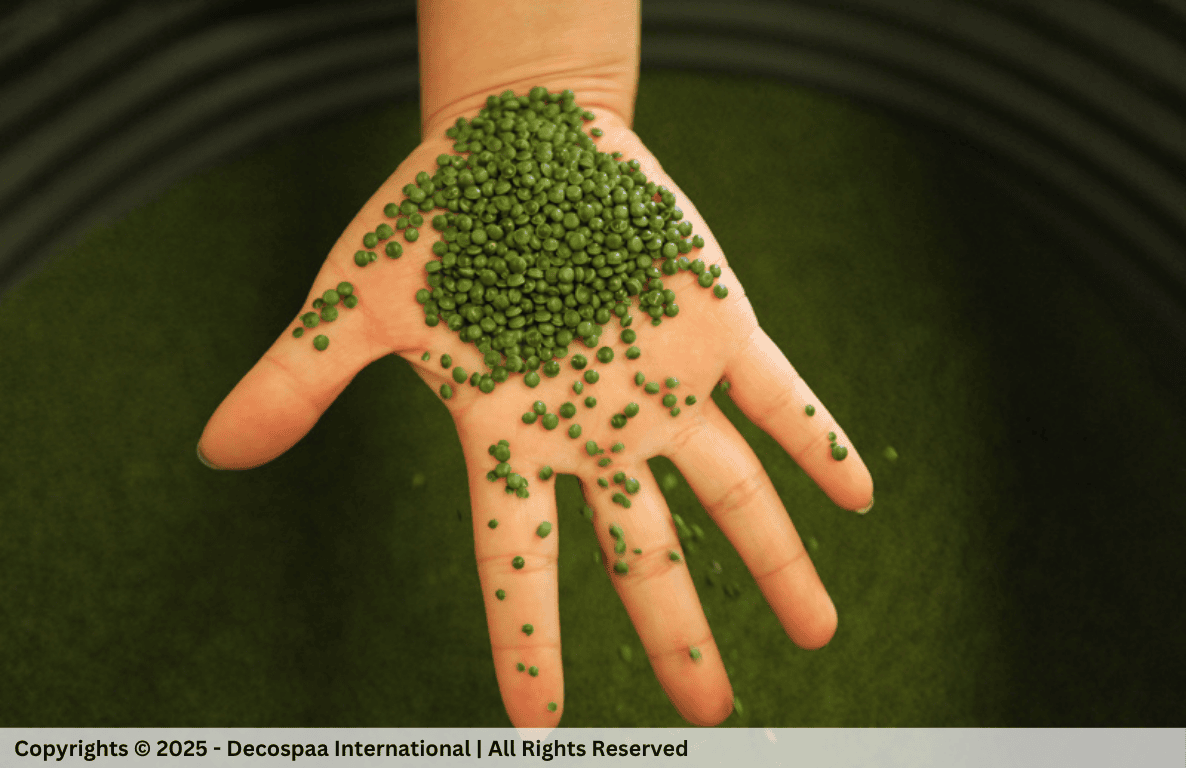
- Raw Material Preparation: Polymer pellets are combined with colorants and UV stabilizers to give the turf its desired color and to protect it from sun damage. These additives help enhance the longevity and appearance of the turf.
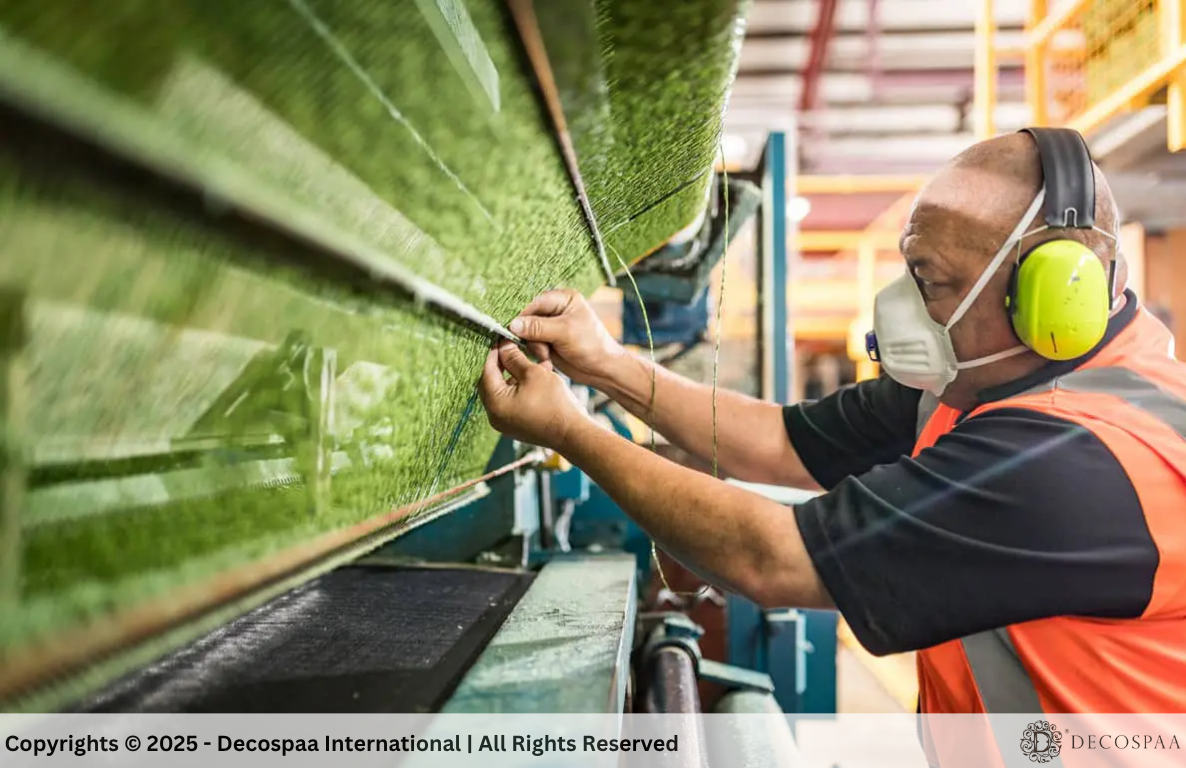
Melting and Shaping: The polymer mixture is melted and then forced through a die, where it takes the shape of either fibrillated yarn or monofilament fibers. The process shapes the material into the desired texture and appearance, which is crucial .
Cooling & Twisting: The fibers are rapidly cooled to solidify, then twisted to create added flexibility and strength fibers to better.
Final Product: After cooling and twisting, the fibers are wound onto spools. At Decospaa, we use modern extrusion equipment to create a wide range of fiber shapes, colors, and durability characteristics.
Conclusion
The extrusion process plays a central role in determining the quality and durability of artificial grass. By selecting the right raw materials and combining them with additives like UV stabilizers, manufacturers can create high-performance synthetic turf that is aesthetically pleasing, durable, and low-maintenance. At Decospaa, we utilize the latest extrusion technology to deliver premium-quality artificial grass for a variety of applications, ensuring long-lasting performance and realistic aesthetics.